Overview
Groovy scripting can be used for various purposes, including automation, customization, and extending the functionality of the platform. Groovy is a versatile scripting language that is commonly used for scripting tasks in SAP Commerce projects.
Groovy scripts can be used for automating routine tasks, such as data import/export, batch processing, and data manipulation. These scripts can save time and reduce manual effort. Groovy scripts are suitable for defining dynamic rules and conditions. You can create rules in Groovy to determine how certain processes should behave based on specific criteria.
Groovy scripts can facilitate integrations with other systems, APIs, and services. You can write scripts to handle data transformations, format data for third-party systems, or perform data synchronization. You can develop custom import and export scripts in Groovy to handle data migration, data synchronization, and data transformation tasks.
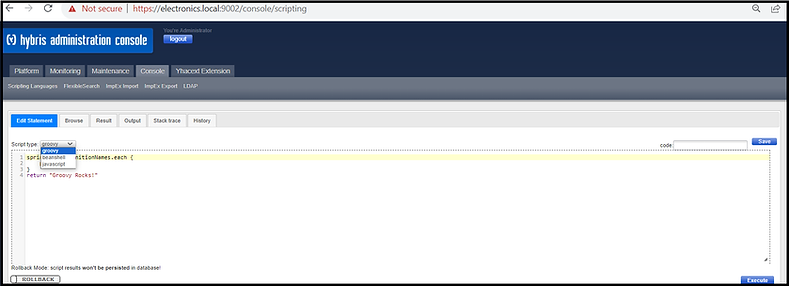
Groovy Script in HAC
1) Go to the HAC
2) Open Console tab
3) Select Scripting Languages
4) Select Groovy in the drop down.
5) Write the script and execute the code
Sample Groovy Scripts
1) Search an item by PK
import de.hybris.platform.core.PK;
Long examplePK = ...........;
sampleObject = modelService.get(new PK(examplePK));
print sampleObject.getPk();
print ", ";
println sampleObject.getName();
2) Execute a Flexible Search query
flexibleSearchService = spring.getBean("flexibleSearchService");
query = "select {pk} from {Category}";
result = flexibleSearchService.search(query);
itempk = "";
for (item in result.getResult()) {
println item.getName();
}
3) Modifying objects
flexibleSearchService = spring.getBean("flexibleSearchService")
mimeService = spring.getBean("mimeService")
modelService = spring.getBean("modelService")
def findMediasWithoutMime() {
query = "SELECT {PK} FROM {Media} WHERE {mime} IS NULL")
flexibleSearchService.search(query).result;
}
findMediasWithoutMime().each {
it.mime = mimeService.getMimeFromFileExtension(it.realfilename)
modelService.save(it)
}
4) Removing items
flexibleSearchService.search("select {pk} from {product} where ....").result.each {
modelService.remove(it)
}
5) Print all properties of an object
result = spring.getBean("flexibleSearchService").search("select {pk} from {Language}")
result.properties.each {
println "$it.key -> $it.value"
}
6) Displaying products without images:
String query = "SELECT {p:pk} FROM {Product AS p}"
params = null;
FlexibleSearchService fss = spring.getBean("flexibleSearchService");
final SearchResult<ProductModel> searchResult = fss.search(query, params);
for (final ProductModel product : searchResult.getResult()){
if(product.getGalleryImages().size() == 0)
{
println product.getCode();
}
};
7) Clearing all product descriptions for all languages.
final Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<String, Object>();
List<Locale> locals = Arrays.asList(Locale.getAvailableLocales());
ArrayList<String> differentIsocodes = new ArrayList<>();
String query = "SELECT {p:pk} FROM {Product AS p}"
params = null;
FlexibleSearchService fss = spring.getBean("flexibleSearchService");
CommonI18NService commonI18NService = spring.getBean("commonI18NService");
CommerceCommonI18NService commerceCommonI18NService = spring.getBean("commerceCommonI18NService");
ModelService modelService=(ModelService)spring.getBean("modelService");
Collection<LanguageModel> languages = commonI18NService.getAllLanguages();
for (LanguageModel language : languages){
differentIsocodes.add(language.getIsocode());
}
final SearchResult<ProductModel> searchResult = fss.search(query, params);
for (final ProductModel product : searchResult.getResult()){
for (Locale locale : locals){
product.setDescription("", locale);
modelService.save(product)
}
};